AI-Enhanced Warehouse & Logistics Operations: Automating Workflows for Speed, Accuracy & Cost Efficiency

AI warehouse automation is moving from isolated pilots to an execution layer that continuously orchestrates warehouse and logistics workflows for speed, accuracy, and cost efficiency across industries. For CIOs, CTOs, COOs, and heads of engineering, the real differentiator is no longer robots on the floor, but the AI decisioning that sits over orders, inventory, routes, and carrier networks.
Why AI warehouse automation now
Global spending on AI in warehousing is scaling fast, with market size estimates around USD 11–12 billion in 2025 and projected CAGRs of roughly 26% through 2030, driven primarily by e‑commerce and rising customer expectations for fast, accurate fulfillment.
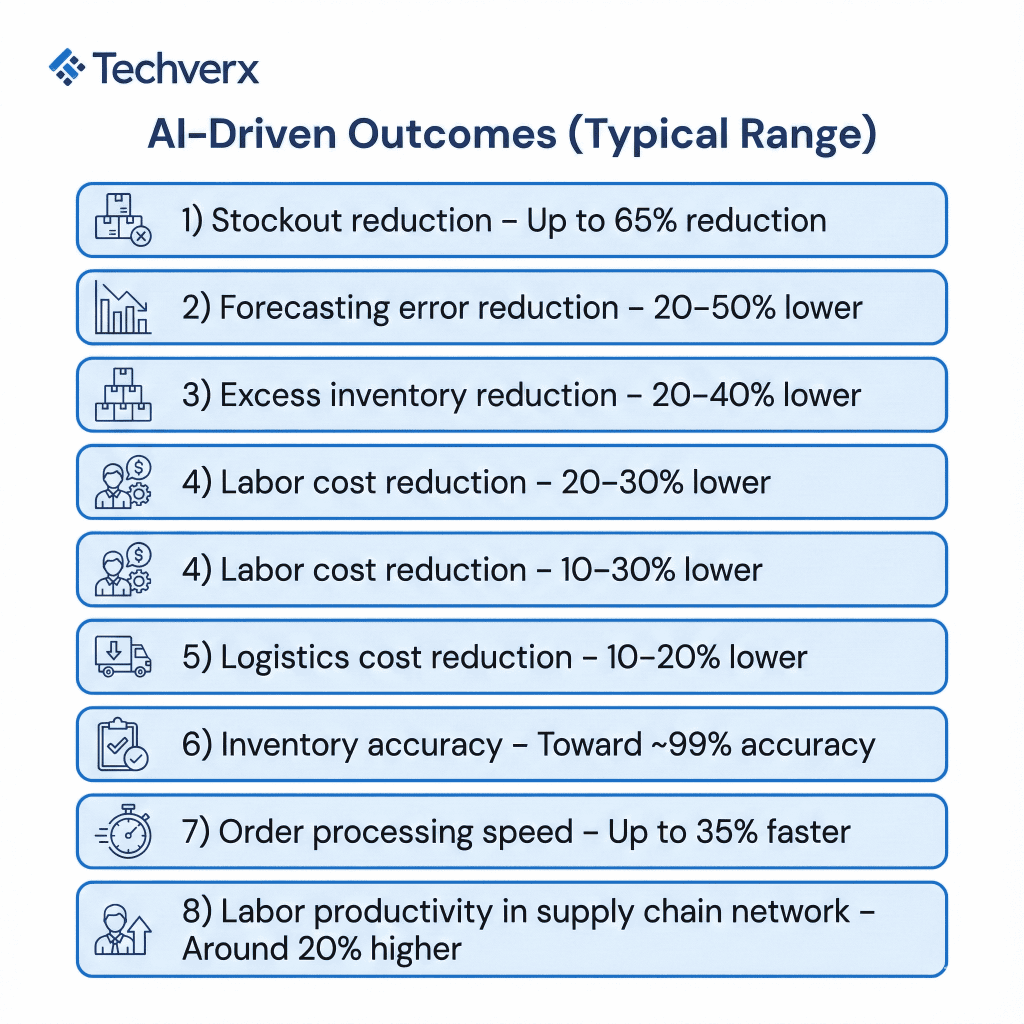
Studies show AI-enabled warehouses can lift inventory accuracy toward 99%, cut labor costs by 20–30%, and reduce fulfillment times by 30–300% when AI-driven routing and automation are fully deployed.
Yet most operations still depend on manual processes, spreadsheet logic, and brittle rules in WMS/TMS/ERP that fracture under stress. The result is familiar: long cycle times, high error rates, inefficient logistics routing, and fire-fighting around exceptions discovered too late in the process.
Where manual and rules-based models break
Traditional warehouse workflow automation relies on static rules, fixed pick paths, rigid allocation priorities, and hand-coded routing logic, that assume demand and constraints behave predictably.
When promotions spike, inventory shifts between nodes, or carrier capacity tightens, those rules break down, leading to mis-picks, split shipments, and re-handling that erodes margin.
Disconnected systems make the problem worse. Many enterprises still run warehouse management, ERP, and carrier systems as separate islands, stitched together by batch jobs and manual reconciliation. That fragmentation creates inconsistent data, duplicate work, and delays in reflecting reality on the floor, perfect conditions for routing errors and late discovery of exceptions.
From robotics focus to decision automation
Most market narratives anchor on robotics, AMRs, AGVs, and automated storage systems, because they are visible and capital-heavy. However, research on AI-driven warehouse automation emphasizes that the biggest structural gains in speed, accuracy, and cost per order come from software-level decision automation: AI deciding what to pick, when, from where, and via which route and carrier, in real time.
Recent reviews highlight AI systems that use machine learning, computer vision, and optimization algorithms to dynamically assign tasks, optimize pick routes, and adapt to real-time constraints.
At scale, this decision layer reduces inventory holding costs, improves service levels, and allows robotics and human labor to be orchestrated as a single, adaptive resource pool rather than static capacity.
AI logistics operations: a unified decision layer
AI logistics operations architecture treats warehouse workflows, transport routing, and carrier selection as one continuous optimization problem rather than separate functions. In practice, this means:
- Continuously ingesting signals from WMS, ERP, OMS, carrier APIs, and IoT devices.
- Applying predictive logistics analytics to forecast demand, volume peaks, lane congestion, and capacity constraints.
- Using AI-powered routing optimization to allocate orders to sites, waves, docks, and carriers based on service promise and cost.
Large-scale implementations show AI-based forecasting can cut stockouts by up to 30% and reduce excess inventory by roughly 20–25%, while AI-driven logistics optimization can reduce logistics-related operating costs by 10–15%. That combination is what converts AI from “efficiency enhancement” into a P&L lever.
Warehouse workflow automation, redefined
Modern warehouse workflow automation goes beyond barcode-driven task queues. AI-driven systems learn the best way to orchestrate work across people, robots, and equipment, and then adapt that orchestration as conditions change.
Key capabilities include:
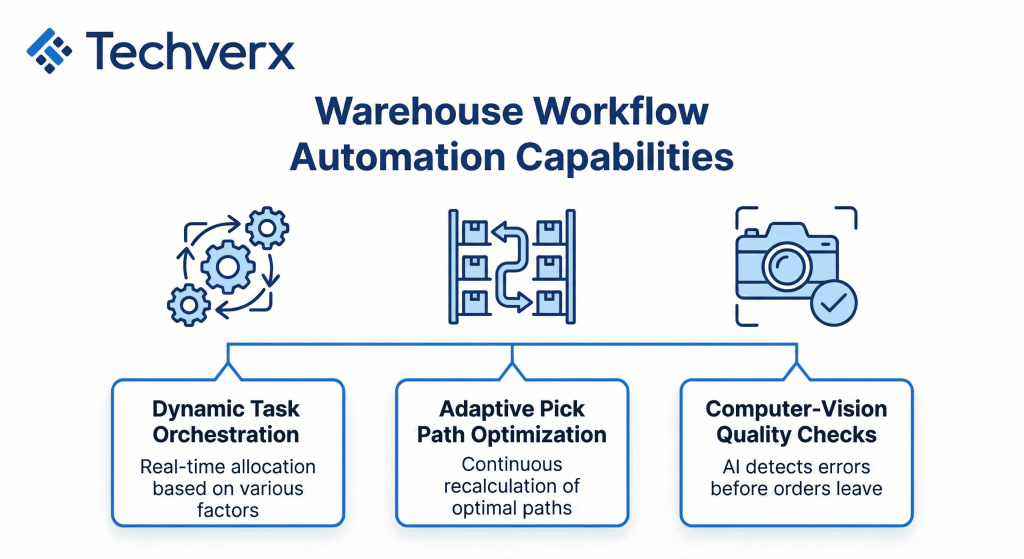
- Dynamic task orchestration: Machine learning models allocate picks, replenishments, put-aways, and cycle counts in real time based on congestion, travel distance, worker skill, and equipment availability.
- Adaptive pick path optimization: Routing AI continuously recalculates optimal paths as new orders drop, inventory locations change, or aisles clog, improving pick speed by 30–50% in some benchmarks while keeping travel distances low.
- Computer-vision quality and accuracy checks: AI vision systems detect mis-picks, mislabels, and damage before orders leave the dock, with defect detection accuracies reported near or above 95%, sharply reducing downstream exception cost.
These capabilities directly attack manual bottlenecks and high error rates without requiring a full “lights out” warehouse.
Routing AI and predictive logistics analytics
On the logistics side, routing AI extends beyond “shortest path” algorithms to include capacity, SLAs, and risk. AI logistics operations platforms use real-time and historical data to:
- Predict lane-level delays, carrier performance variability, and capacity constraints days or weeks ahead.
- Optimize order-to-route assignment so that urgent or high-value orders automatically flow to the most reliable combinations of node and carrier.
- Re-plan routes mid-execution as disruptions unfold, instead of waiting for exceptions to surface in end-of-day reports.
Studies in AI operations management show that AI can cut forecasting errors by up to 50% and lost sales due to shortages by up to 65%, while also enabling near-perfect on-time fulfillment in some large-scale deployments. Those same techniques, applied to routing and load planning, create measurable drops in fuel, dwell time, and premium freight spend.
Closing the exception-handling gap
Exception handling is where many operations lose margin, late discovery of shortages, misrouted pallets, or capacity failures forces expensive workarounds. AI-enhanced warehouse and logistics operations handle exceptions differently:
- Early detection: Anomaly detection models scan scans, scans-to-location mappings, sensor data, and event streams to flag likely mis-picks, shorts, or dwell anomalies in near real time.
- Root-cause context: AI surfaces correlated signals SKU, site, shift, carrier, lane so teams can resolve underlying issues instead of repeatedly treating symptoms.
- Policy-driven escalation: Intelligent workflow automation routes exceptions to the right team or process step with suggested remediation actions based on historical resolution patterns.
This reduces the proportion of issues discovered “at the customer” and shifts effort upstream, where corrections are cheaper and less damaging to service levels.
Techverx: AI decisioning across warehouse and logistics
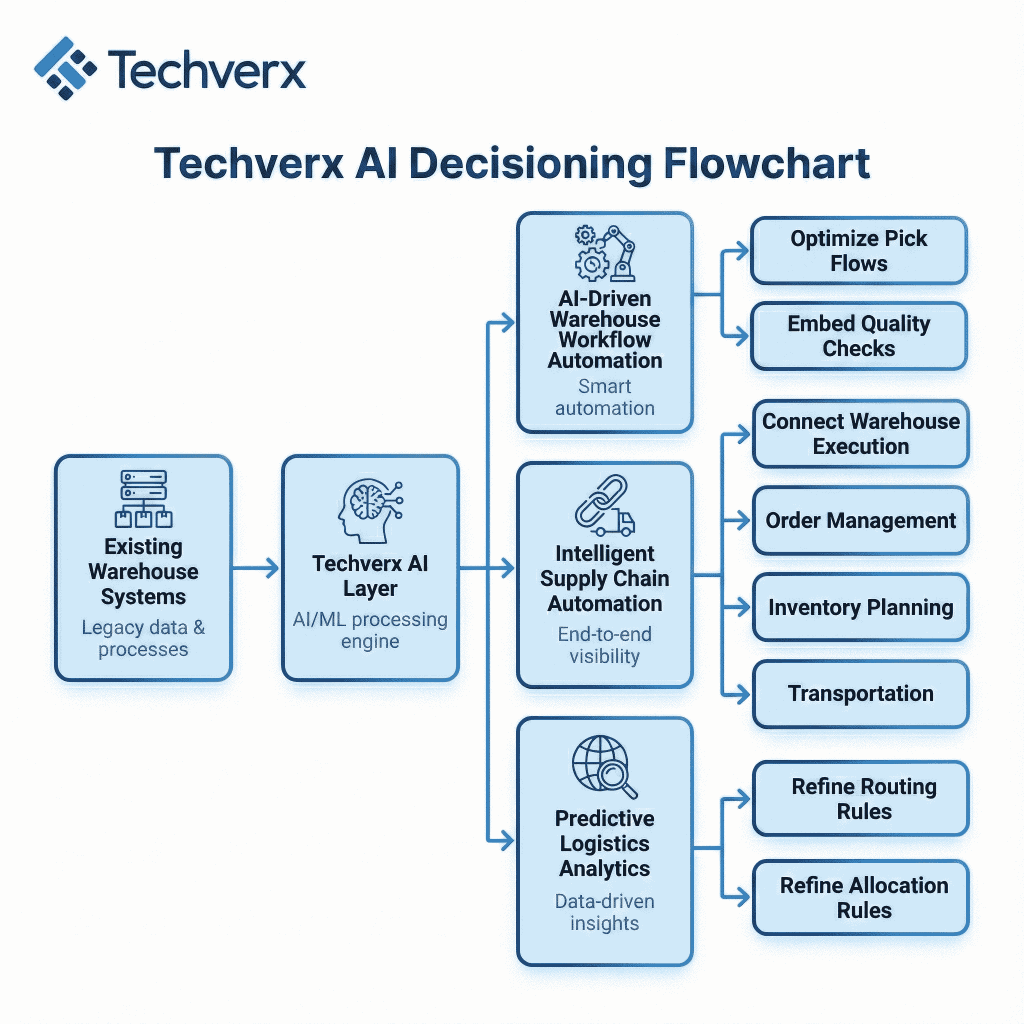
Techverx specializes in building custom automation and AI layers that sit above existing warehouse, ERP, and carrier systems, rather than forcing rip-and-replace. For enterprises wrestling with fragmented stacks and rising logistics costs, this means:
- AI-driven warehouse workflow automation that integrates with your WMS and operational systems to orchestrate tasks, optimize pick flows, and embed quality checks.
- Intelligent supply chain automation that connects warehouse execution with order management, inventory planning, and transportation so that routing and capacity decisions are made with a full-picture view.
- Predictive logistics analytics and AI-powered routing optimization capabilities that leverage historical performance and real-time signals to continuously refine routing and allocation rules.
Because Techverx operates as a product engineering and integration partner, teams can design AI agents, optimization services, and workflow automation that reflect each company’s constraints, multi-tenant SaaS, hybrid cloud, regional carriers, or strict regulatory environments rather than pushing a one-size-fits-all platform.
From static rules to intelligent workflows
Moving from rule-based automation to intelligent workflows is as much a design problem as a data problem. Successful programs typically:
- Start with a narrow, high-impact flow such as outbound picking and routing on one high-volume lane, and benchmark improvements in pick time, error rates, and logistics cost per order.
- Wrap existing systems with APIs and event streams so AI services can read and write decisions without destabilizing core ERP or WMS.
- Introduce human-in-the-loop controls, ensuring operators can override, approve, or train AI when edge cases appear, which accelerates model learning while maintaining operational trust.
Research across AI operations shows that organizations combining AI automation with structured human oversight realize higher ROI and avoid the brittleness of fully autonomous but opaque systems.papers.
What leaders should prioritize next
For C-suite and architecture leaders, the priority is not buying more disconnected tools, it is designing an AI decision layer that turns warehouses and logistics networks into a coordinated, learning system. Concretely, that means:
- Defining the critical workflows where seconds and percentage points matter most: picking, dock scheduling, carrier selection, and lane routing.
- Building a unified data foundation that connects warehouse events, inventory positions, orders, and carrier performance into a single analytics and decision stack.
- Partnering with engineering teams capable of implementing routing AI, warehouse workflow automation, and predictive logistics analytics as production-grade services, not point pilots.
Enterprises that take this path are already reporting double-digit gains in productivity, lower operating costs, and more resilient service levels, even as labor markets tighten and logistics volatility continues.
For organizations ready to move beyond rules-based automation, AI-enhanced warehouse and logistics operations are becoming the execution backbone that keeps promises to customers while protecting margins.
If this resonates with your roadmap, let’s line up a quick working session with your team!

Rachel Kent
Rachel Kent is a Technology Advisor at Techverx based in McKinney, Texas, specializing in digital strategy, scalable architectures, and “right-fit” solutions. With a background as a Software Engineering Lead and full-stack engineer across healthcare and tech, she bridges business goals with modern stacks to rescue stalled projects, modernize legacy systems, and deliver ROI-focused outcomes.
Hiring engineers?
Reduce hiring costs by up to 70% and shorten your recruitment cycle from 40–50 days with Techverx’s team augmentation services.
Related blogs